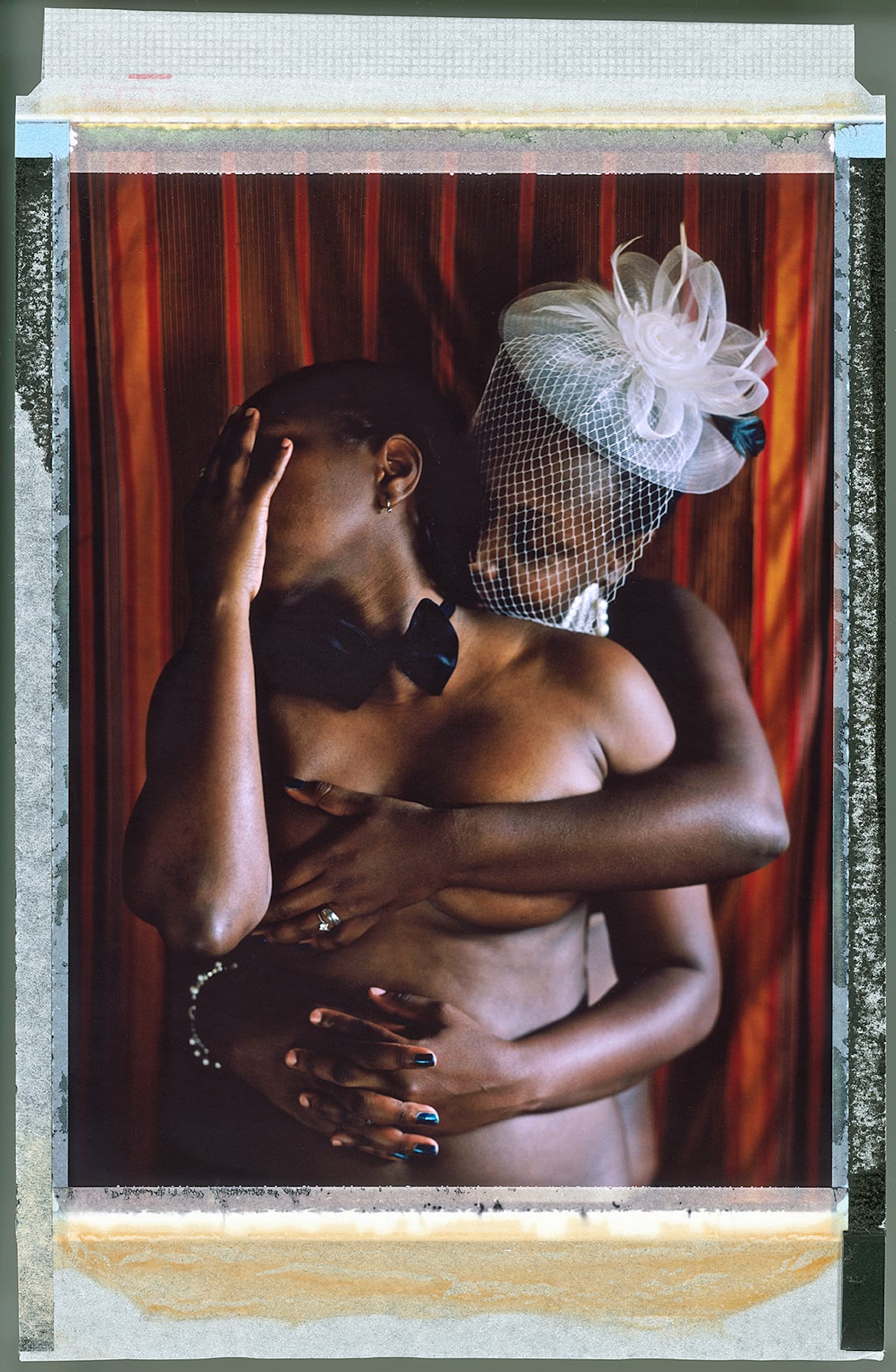
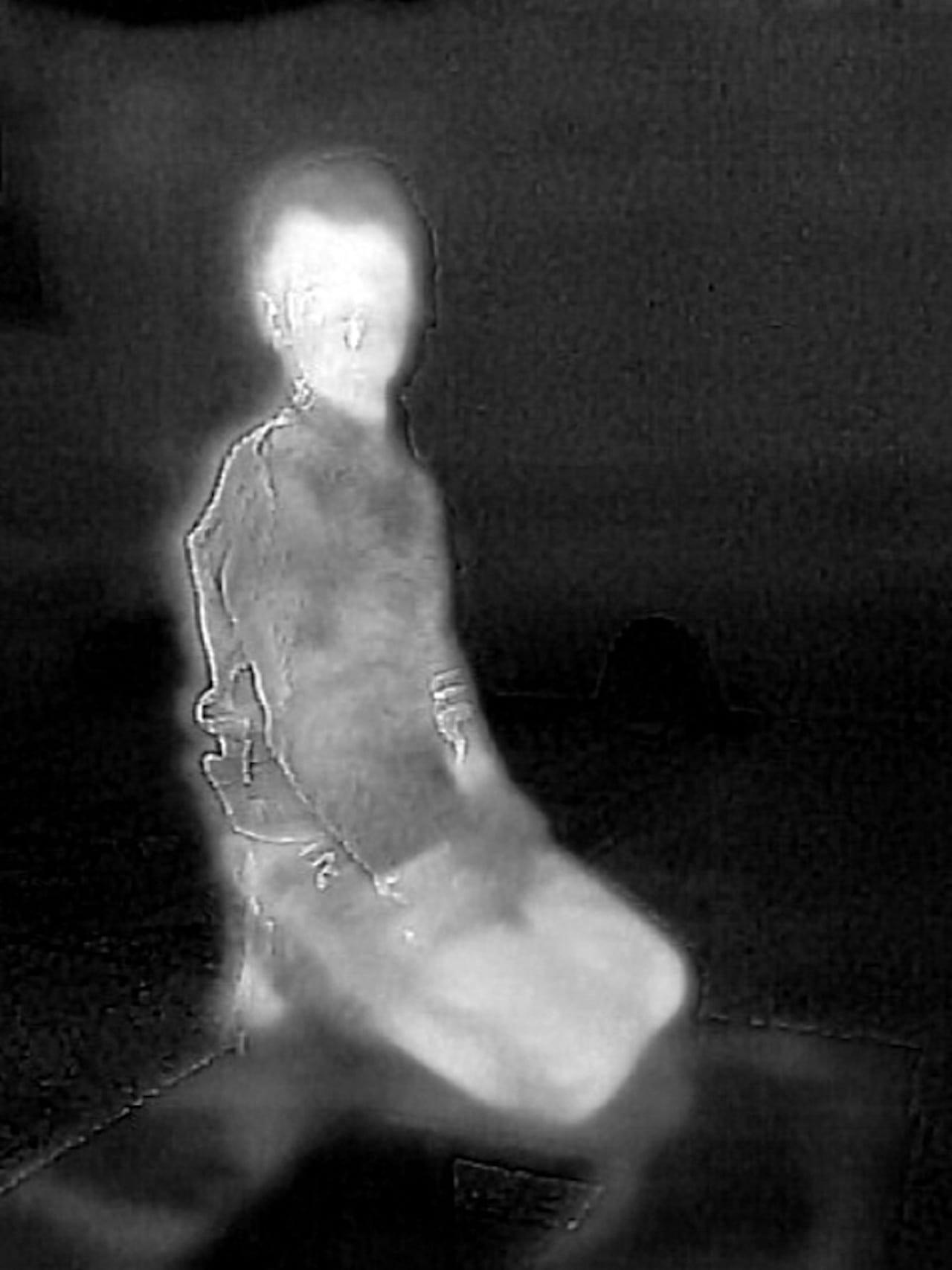
When Robin Hammond started work on his project Where Love Is Illegal, he changed his approach to photography. Shooting members of the LGBTI [lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex] community who have faced persecution and punishment in countries in which such prejudice is enshrined in law, he relinquished much of the creative control to the sitters.
Up until then, he’d worked in the tradition of great photojournalists, committing extended periods of time to documenting stories as they unfolded in front of his lens. His acclaimed project Condemned, for example, a study of the treatment of the mentally ill in Africa, was shot over 10 years. But during his numerous trips to the continent, he had become acutely aware of the deep-rooted homophobia there.
“Wherever I went, I was surprised by how extreme the views on homosexuality were,” he says.