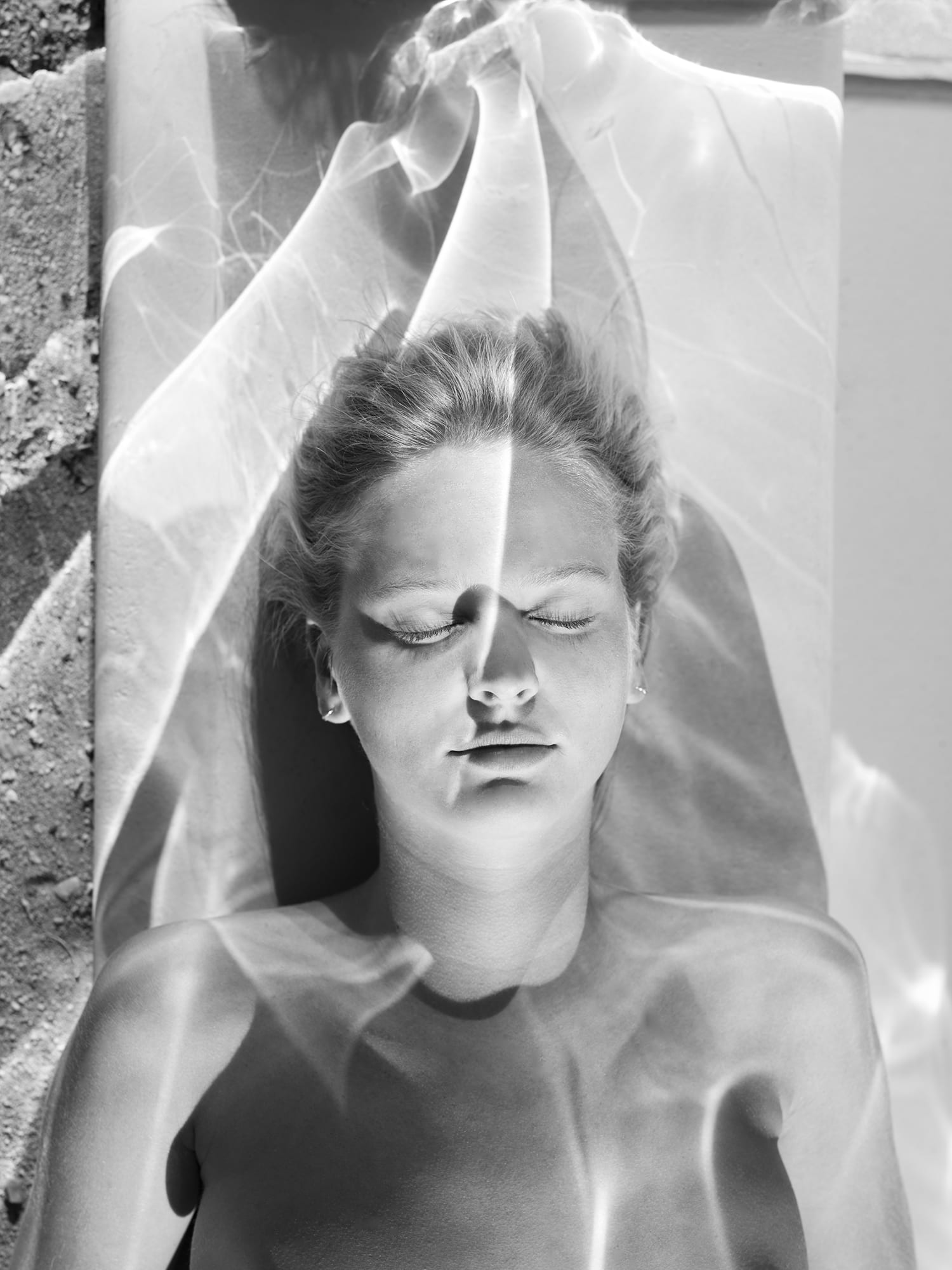
“I got into photography because I’m a little restless, and I liked that it was fast,” says Brazilian photographer Mona Kuhn, who has just published her sixth book with Steidl, She Disappeared Into Complete Silence. Even so, the speed of photography haunted her, as Kuhn feared that her photographs would be consumed then discarded – like so many of the magazines she read and tossed away. “I wanted to stop time with photography,” she says. “That’s another reason I got into nudes, for the timeless aspect.”
She Disappeared Into Complete Silence is an experimental project shot in Acido Dorado, a reflective house in the middle of the Californian desert designed by American architect Robert Stone. Inside it are mirrored ceilings and walls, which refract sheets of golden desert light that flood the house. Here, Kuhn presents a solitary nude on the edge of the desert, removed from any symbols of time, creating “an abstraction of being,” and “a space where our mind resides”.